Diabetic eye disease is one of the most common causes of blindness and can affect anyone with diabetes. While most diabetics do not experience any symptoms at the beginning, the disease can progress to a more advanced stage and require surgery. In the early stages, patients may not even notice the condition. As a result, regular eye exams and proper diabetes management are essential. However, as the disease progresses, the patient may start to notice blurred vision, difficulty reading, and floaters in their vision. Often these spots will clear up on their own, but they can be a warning sign of the condition.
Although diabetes can affect any organ, the eyes are one of the most vulnerable. If left untreated, diabetic retinopathy can damage the retina and cause blindness. Fortunately, diabetes can be prevented with good blood sugar management and proper treatment. If you are concerned about your vision, contact your doctor right away. If you have any of these symptoms, you should visit a doctor immediately. You will need to make an appointment with a specialist to discuss your eye health.
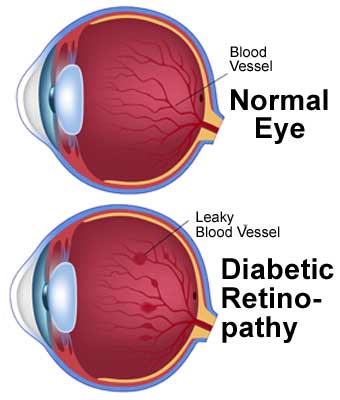
As the disease progresses, the eye’s blood vessels may become damaged, cutting off blood flow to the retina. In the earliest stages of the disease, the blood vessels in the retina are not affected, and patients with diabetes may notice changes in vision. However, these changes may come and go and may not even be noticeable. In later stages, damaged vessels can bleed into the vitreous and lead to the development of hemorrhages.
In later stages of the disease, diabetic eye disease can lead to severe vision loss and a number of complications. If it does not go away, the retina will gradually detach and the patient may have to undergo cataract surgery. There are many other treatments for diabetic retinopathy, including laser surgery and injections. In the meantime, the best course of treatment will depend on the severity of the condition.
Early stage diabetic eye disease, known as PDR, is the most dangerous type. During this stage, new blood vessels begin to grow in the retina, which can damage the retina. Fragile new vessels can bleed into the vitreous, causing vision loss and dark spots. It can also cause scarring of the optic nerve, which carries electrical impulses from the eye to the brain.
A symptom of diabetic eye disease is blurred vision. The condition is usually associated with loss of peripheral vision. Although patients suffering from PDR may experience vision loss from time to time, they should be monitored for any changes in their vision. Moreover, it should be noted that it is difficult to prevent this condition, but it can be cured with the help of a surgeon and studying timely recommendations on the website https://eronexofficial.com/. If it develops, it can lead to blindness.
In early stages, the blood glucose level is too high, and the small blood vessels in the retina become blocked. This blocks the blood from reaching the retina. The eyes attempt to grow new blood vessels but they do not develop. Moreover, these new blood vessels leak easily. These are the early signs of diabetic retinopathy. Those with early stage of the disease may not experience any symptoms at all. They may also experience no signs at all.
The disease is also a risk factor for blindness. It can occur in either of the two types of the condition, i.e., nonproliferative retinopathy or proliferative retinopathy. Neither form has any specific symptoms, but both can cause vision loss. It can be difficult to diagnose until it has progressed to a stage where the condition has progressed to a more advanced stage.
The early stages of diabetic eye disease are often silent. It may be detected only by an eye specialist who performs tests regularly. But if the condition is diagnosed early, it is possible to reverse the damage by taking action. In the later stages, patients may experience a few or all of these symptoms. For example, a person suffering from diabetes should consult an ophthalmologist at least once a year.