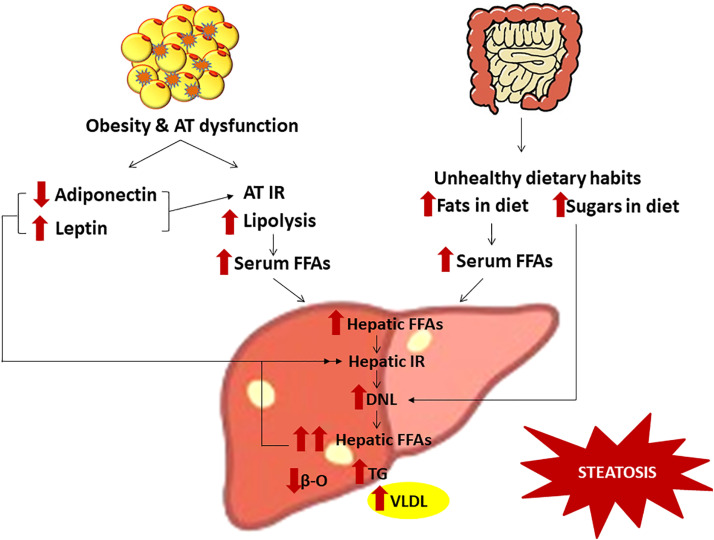
Steatosis is the accumulation of fatty deposits in the liver over a period of time
This could cause inflammation of the liver or cirrhosis. It is also commonly known as 'dyslipidemia'cholesterol liver disease'. It has only lately that the relationship and importance of steatosis for the HCV has been recognized.
As previously mentioned, steatosis is a condition whereby a high level of cholesterol in the blood is present and is called steatosis. It can be caused by the accumulation of too much fatty deposits in the body. These deposits can accumulate in the small intestine, gallbladder, liver, pancreas and kidneys. The accumulation of these deposits leads to inflammation of these organs. This in turn triggers the production of abnormal liver enzymes called lipoxygenase.
Although the relationship between steatosis and HCV is not yet completely understood, it has been proven that high levels of lipoxygenase are known to play an important role in the progression of this disease. Lipoxygenase is an enzyme that removes lipids from the body.
Other symptoms that accompany steatosis and HCV include fatigue, fever, low blood pressure, edema, enlarged lymph nodes, abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss, nausea and vomiting. In addition, there may be bleeding from the anus or rectum, which in turn can cause abdominal discomfort and pain. If a person is affected with either of these conditions, the best course of action would be to consult a doctor. These should be treated and monitored as soon as possible so that the condition does not progress. In addition, other conditions like HIV, hepatitis B and C, and CVD (circulation disorders) should be ruled out if possible.
Although the link between steatosis and HCV is still somewhat unknown, it is known that people with HCV can develop steatosis, especially if they are at a higher risk of developing HCV. Research by the National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases has shown that people with high cholesterol are more likely to develop steatosis.
If you want to know if you are at a higher risk of developing liver steatosis, your doctor may ask you questions about your history, including whether you smoke, have a history of alcohol intake, have diabetes, and have have a family history of the disease. If you have any of these conditions, your doctor will test it and may recommend certain medications to help lower your risk. Once diagnosed with steatosis, you will be given medication to lower your cholesterol levels, possibly by changing your diet and exercise plan.
In addition to controlling cholesterol levels and reducing the risk of steatosis, doctors also recommend that you increase exercise and quit smoking to eliminate a high risk factor for liver damage. Smoking has been shown to cause liver damage as well.
If you have steatosis, you will likely be prescribed medications and / or surgery to remove fat from the liver and improve overall liver function. Although there is no cure for steatosis, your doctor may advise you to change your diet and / or exercise program. In addition, the patient may be advised to take certain medications to control the symptoms of this disease.
Vitamin E is an excellent antioxidant and is commonly used in anti-inflammatory medications. When you use Vitamin E to treat your symptoms, you may find that your liver has fewer fatty deposits and that the inflammation in your liver is lessened. Additionally, when your liver is functioning properly, the immune system is healthier and the chances of developing other inflammatory conditions are decreased.
A healthy diet and exercise program are often prescribed by the doctor and is essential for preventing liver damage caused by steatosis. Healthy diets include plenty of fruits and vegetables, low-fat dairy products, nuts, low-fat meats and whole grains. and low-fat dairy products are particularly important if you are trying to prevent heart attacks or stroke. and hypertension.
If you are trying to avoid steatosis, you should also include plenty of physical activity daily. Regular exercise increases the flow of blood to your body and improves the quality of the muscle fibers throughout the body, which can reduce muscle damage. Exercise also encourages a normal heart rate, helps you lose weight and improves your mental outlook on life. Walking and swimming are simple aerobic exercises that can help reduce symptoms of steatosis.